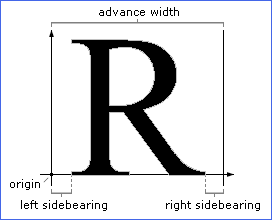
advance width
The width of a letter including its surrounding space. The surrounding space on the left is called the left sidebearing. On the right it is called the right sidebearing.
ascender
The part of lowercase letters (such as b, d, f and k) that ascends above
the x-height of the other lowercase letters in a font.
ascent
A font's maximum distance above the baseline.
baseline
The imaginary line upon which the characters of a font rest. The
baseline-to-baseline distance can be calculated as ascent - descent +
linegap.
cap height
The height from the baseline to the top of the uppercase letters in a
font. This may or may not be the same as the height of ascenders.

descender
Part of letters (such as y, p, q) that descends below the baseline of
the other letters in a font.
descent
A font's maximum distance below the baseline. By convention the descent
is negative.
diacritic
A mark normally used in conjunction with another glyph. In Latin fonts
these are sometimes called 'accents'. In Hebrew and Arabic these are
marks that denote vowels.
glyph
A graphic symbol that provides the appearance or form for a character.
A glyph can be an alphabetic or numeric font or some other symbol that
pictures an encoded character.
kerning
Kerning is the reducing/ increasing of the space allocated between two
glyphs to improve the visual appearance.
leading
The internal leading is the space you have above a character to fit in
accents, diacritics, etc. Internal leading is equal to usWinAscent +
usWinDescent - unitsPerEm. External leading is the distance between two
lines of text and is equal to MAX(0, LineGap - ((usWinAscent +
usWinDescent) - (Ascender - Descender))).
left sidebearing
See sidebearings.
line gap
See leading.
right sidebearing
See sidebearings.
sidebearings
The distance between the origin and the left edge of a character (left
sidebearing) and the distance between the width line and the right edge
of a character (right sidebearing).
word space
The white space between two words placed on the same horizontal line
x-height
The flat height of the lowercase glyphs, usually the same as the top of
the lowercase x.



